When I had to contact amazon customer service, in the past, I would directly call their number, 844-311-0406. As they provide 24/7 support (of course), it would be easy to get in touch with a customer service representative (CSR). I would have to wait on hold for a bit, but not too long. The longest I waited was around 15 minutes.
Now, that was the past me. It took me a while to explore the other options amazon customer service offers, but I found some that are even easier and more convenient. For a long time, contacting Amazon via live chat was the most convenient option for me. The best way to contact any company would be through their live chat support. However, you can no more find the link to it on the amazon customer service page, unfortunately. They have apparently eliminated their live chat option altogether.
So, what is the most convenient way to contact amazon customer service?
There is one way that is fast, but maybe not the most comfortable one for all. Other is the easiest, and the most convenient method. Let’s look at each:
Fastest way

The fastest, by far, is calling Amazon directly. But it is very understandable that some people are not fans of talking on the phone. Not only because of the required effort and wait time, but also because it is more difficult to keep track of the conversation. And amazon customer service is not the best at keeping track of the conversation, to be honest.
The easiest way

The best, and easiest way to contact amazon customer service is by email. You can find the link to the contact page on the amazon customer service page. You can follow this link.
I have found that the email method is the best because you can keep track of the conversation easily. You can also include all the necessary information in the initial email so that the CSR can help you resolve your issue as quickly as possible.
For example, I had an issue with my order not being delivered on time. I contacted amazon customer service via email and included my order number. That particular order was of my yoga costume, they had sent it torn. The issue simply required multiple threads of conversation; it could not have been possible with a call.
However, according to Amazon, calling is still the best option for general inquiries about Amazon Go, Amazon Go Grocery, and Amazon Fresh.
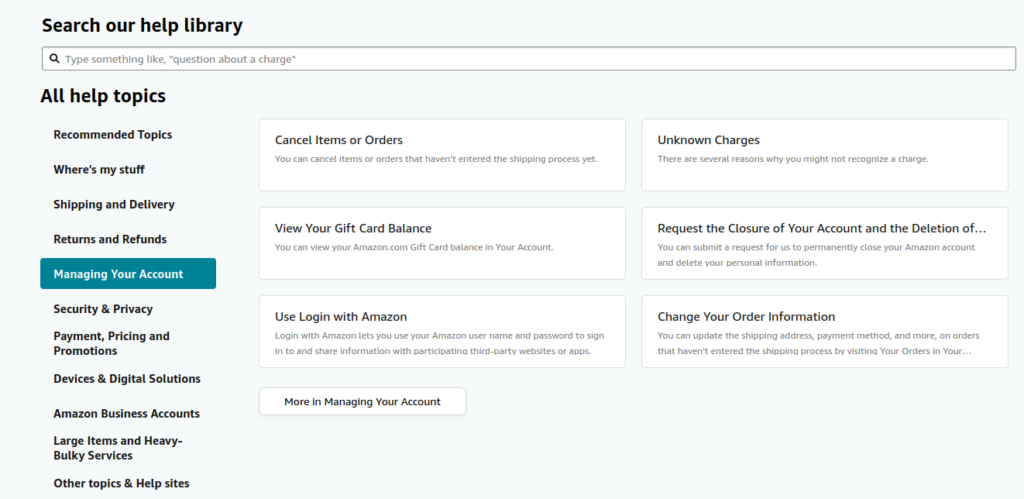
The customer support page: How to find what you need help for?
The navigation of the customer support page by amazon is pretty impressive. There are separate options for:
- A delivery, order, or return
- Prime
- Payment, charges, or gift cards
- Login, address, security & privacy
- Memberships, subscriptions, or communications
- Kindle, Fire, or Alexa device
- eBooks, Prime Videos, or Music
- Accessibility
- Something else

That’s pretty normal. But impressively enough, in their “All help topics” section, I don’t know what AI algorithm they use there, but it has answers to pretty much every question a normal customer could have about their service, as well as products. I think they were pretty smart with it; AI taking away the jobs of customer support staff. But who cares, as long as we, the customers, are getting our problems resolved efficiently?
Bottom Line
Hope this article was fun, apart from being helpful!