The impact of large language models (LLMs), particularly transformer-based models like GPT-4, has been witnessed across various fields, such as chemistry, biology, and code generation. Recently, another noteworthy advancement has emerged: the creation of Coscientist, an artificial intelligence system driven by GPT-4, which autonomously designs, plans, and executes complex experiments across diverse scientific tasks.
According to a study published in the journal Nature on December 20th, Coscientist excels in accelerating research, particularly in the optimization of reactions, presenting autonomous capabilities in experimental design and execution. The system integrates large language models with tools like internet and documentation search, code execution, and experimental automation.
In a catalytic cross-coupling experiment aimed at synthesizing biphenyl through Suzuki-Miyaura and Sonogashira reactions, Coscientist displayed remarkable autonomous capabilities. Utilizing internet searches and data analysis, the system autonomously selected appropriate reactants, reagents, and catalysts from available resources.
Results showed strict reasoning
Coscientist consistently avoided errors in reactant selection (e.g., never choosing phenylboronic acid for the Sonogashira reaction). Varied preferences in selecting specific bases and coupling partners were observed across different experiments.
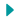
Coscientist’s capabilities in chemical synthesis planning tasks.
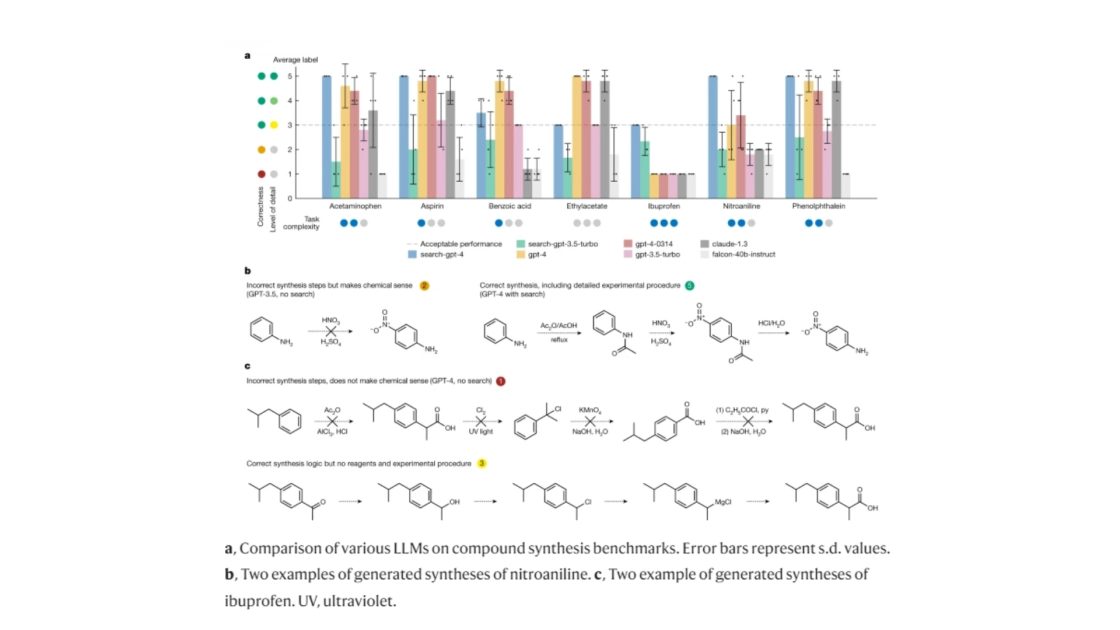
Interestingly, the system provided justifications for its choices, displaying its reasoning regarding reactivity and selectivity.
Experimental execution and validation
Following its autonomous experimental design, Coscientist wrote a Python protocol for the liquid handler, specifying the necessary volumes for the reactions. Upon minor errors in protocol (e.g., incorrect heater-shaker module method name), Coscientist consulted documentation autonomously and rectified the protocol.
Figure/Description Credit: nature.com
Gas chromatography-mass spectrometry analysis of the reaction mixtures confirmed successful synthesis of target products for both Suzuki and Sonogashira reactions. Signals corresponding to the molecular ions of biphenyl and Sonogashira reaction products were observed in the chromatograms.
Revolutionizing research?
The integration of LLMs like GPT-4 with scientific tools signifies a potential revolution in scientific research. These systems offer rapid problem-solving, autonomous experimentation, and advanced reasoning, indicating promising strides toward further scientific discovery and innovation.
The responsible use of these systems is essential to cope with potential risks associated with their misuse. Ethical considerations and safety implications must be addressed as technology continues to advance.
- AI-Powered PCs: Overhyped Trend or Emerging Reality? - August 21, 2024
- Princeton’s AI revolutionizes fusion reactor performance - August 7, 2024
- Large language models could revolutionize finance sector within two years - March 27, 2024