It’s natural to worry about the effects of aging on our bodies and minds. But there’s hope in recent scientific progress, especially in the area of anti-aging. Scientists have been working on pills that target mitochondria, the tiny powerhouses within our cells, to potentially slow down the aging process.
Understanding aging and mitochondria

Aging involves a gradual decline in both our physical and mental abilities. One important part of this process is the mitochondria, often called the “powerhouse of the cell.” These tiny structures are in charge of making energy in the form of ATP through a process called oxidative phosphorylation. But as we get older, this process becomes less efficient. That means we make less energy and produce more harmful substances called reactive oxygen species (ROS), which can harm cells. Scientists call this the mitochondrial theory of aging.
For instance, studies have found that in diseases like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s, which are linked to getting older, there’s a big drop in how well mitochondria work. So, figuring out how mitochondria are involved in aging is really important for finding ways to treat age-related diseases.
The role of mitochondria in aging
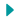
As we age, our mitochondria can start to malfunction. This happens because of things like DNA mutations and increased levels of harmful substances called reactive oxygen species. This damage to mitochondria can speed up the aging process. And our body’s defense system, called the immune system, gradually gets weaker. In scientific terms, this natural aging process is referred to as immunosenescence. One reason for this decline is that mitochondria don’t work well.
Research has shown that as people age, their immune cells have fewer mitochondria. This means our immune system then might not work as effectively, which can make us more likely to get sick.
So, taking care of our mitochondria could be really important for keeping our immune system strong as we age. That’s where mitochondrial rejuvenation comes in. By boosting the function of our mitochondria, we might be able to improve our immune response, even as we get older.
Mitochondrial rejuvenation as an anti-aging strategy
Mitochondrial rejuvenation is an exciting area of research in anti-aging treatments. The idea behind this is to fix and improve how mitochondria work to fight the effects of getting older.
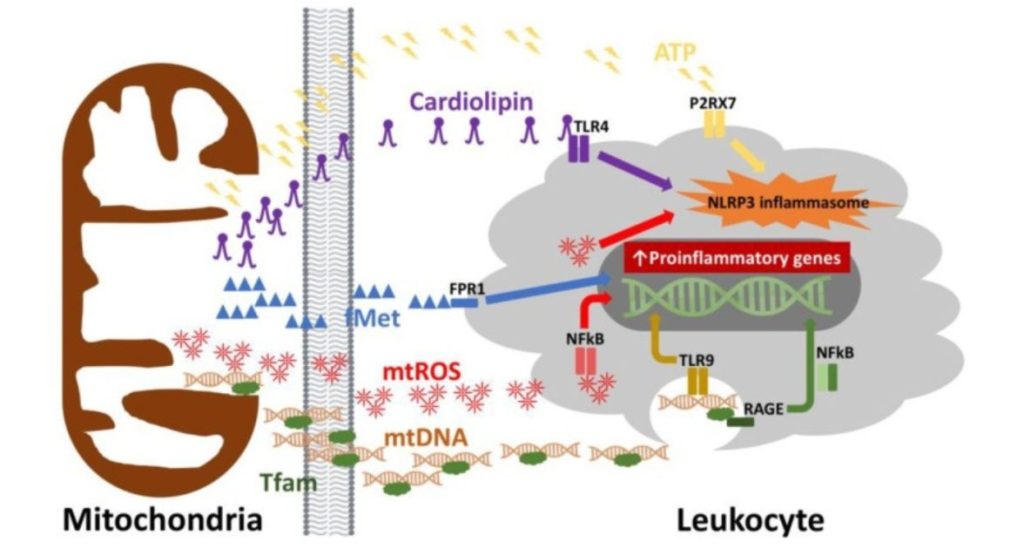
Scientists, for example, are looking into certain substances that might boost how mitochondria function. One of these is Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide (NAD+), which is important for making energy in mitochondria. As we get older, our bodies have less NAD+, which means our mitochondria work less effectively. Giving NAD+ or things that help make it has been proven to make mitochondria work better and improve overall health in older mice.
Another possible idea would be to use antioxidants that target mitochondria. These substances can stop harmful chemicals made by mitochondria, which can damage cells and maybe slow down aging.
Also, scientists are studying stem cells for mitochondrial rejuvenation.
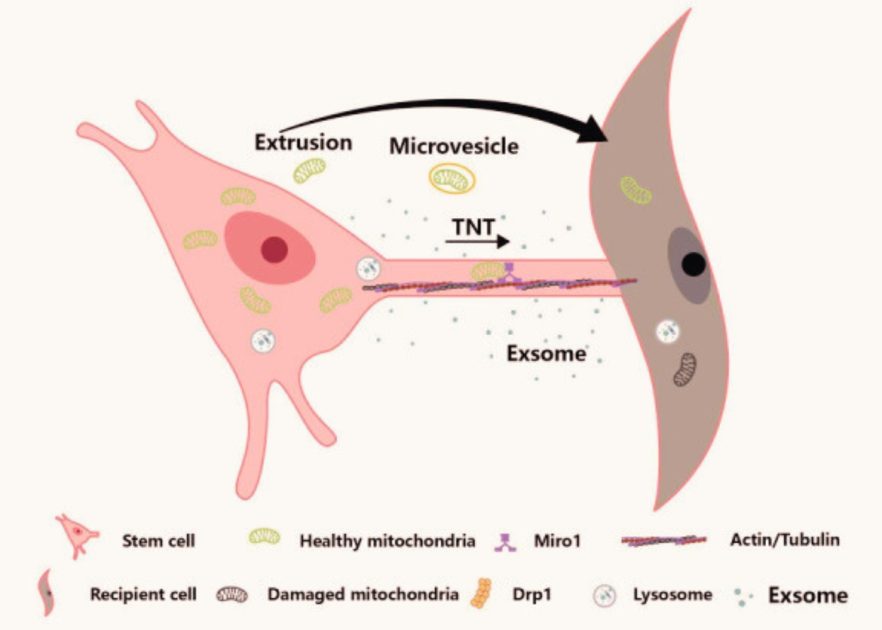
Stem cells can make more of themselves and turn into different types of cells, and their mitochondria seem to work better than those in other cells. So, treatments that involve putting stem cells or their mitochondria into older tissues and organs might make them younger again.
These are just a few examples of what researchers are looking into to rejuvenate mitochondria. Even though we’re still early in this research, the future of anti-aging treatments looks bright with these ideas.
The future of anti-aging pills
Indeed, the outlook for anti-aging treatments focusing on mitochondria appears promising. For example, research indicates that using substances like Coenzyme Q10, an antioxidant supporting mitochondrial function, can enhance the health and lifespan of mice.
Similarly, trials involving humans and supplements like Nicotinamide Riboside, a precursor of NAD+ crucial for mitochondrial energy production, have displayed potential advantages in bolstering mitochondrial health and decelerating aging.
In addition, technological advancements, such as the creation of nanocarriers for targeted delivery of drugs to mitochondria, are opening doors to more efficient therapies. These innovations have the potential to refine the precision and effectiveness of anti-aging treatments, offering hope not only for slowing down aging but even potentially reversing it.
References:
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41392-023-01343-5
https://www.nature.com/articles/s43587-022-00340-7
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-023-31510-1
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6627503/
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8773271/
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9512238/
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9519729/
https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/sciadv.add5163
https://pubs.rsc.org/en/content/articlehtml/2024/ma/d3ma00629h
- AI-Powered PCs: Overhyped Trend or Emerging Reality? - August 21, 2024
- Princeton’s AI revolutionizes fusion reactor performance - August 7, 2024
- Large language models could revolutionize finance sector within two years - March 27, 2024